What is Security Awareness Training?
- Delivered at the ease of their workstations
- Monthly simulated phishing attacks
- A highly interactive web-based training module
- Short assessments to measure the level of absorption
- Detailed reports, showing stats and graphs for both training and phishing, ready for management
This ensures your employees understand the fundamental mechanism of spam, phishing, malware social engineering and etc. Thus, providing a wholesome cybersecurity training experience.
Why Security AwarenessNow!

Compliancy
Risk Management in Technology (RMiT) policy by Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM)
Under Section 13: Internal Awareness and Training, it specifies that:

ISO 27001/27002:2013 Requirements by International Organization for Standardization
Under Clause 7.2.2: Information Security Awareness, Education and Training, it specifies that:
'All employees of the organization and where relevant, contractors should receive appropriate awareness education and training and regular updates in organizational policies and procedures, as relevant for their job function’.
View ISO 27001:2013 Requirements
View ISO 27002:2013 Requirements

Malware: Ransomware
Malware is any software intentionally designed to cause damage to a computer, server, client, or computer network. Malware does the damage after it is implanted or introduced in some way into a target's computer - usually through an email and can take the form of executable code, scripts, active content, and etc
Service Overview
Our Continuous Training approach informs users about best practices and teaches users how to employ these practices when they face security threats.
A continuous cycle of assessment, education, reinforcement, and measurement maximizes learning and lengthens retention. Thus providing the flexibility to:
- Evolve your program over time
- Identify areas of susceptibility
- Deliver targeted training when and where it’s most needed.

Service Overview
Our Continuous Training approach informs users about best practices and teaches users how to employ these practices when they face security threats.
A continuous cycle of assessment, education, reinforcement, and measurement maximizes learning and lengthens retention. Thus providing the flexibility to:
- Evolve your program over time
- Identify areas of susceptibility
- Deliver targeted training when and where it’s most needed.

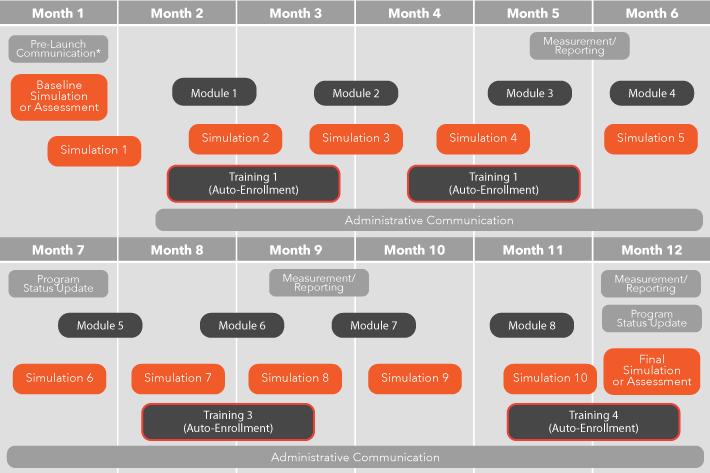
STEP 1
ASSESS
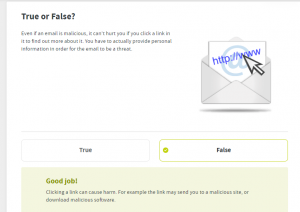

Phishing
Lure targeted user to click on a link in an email

Credential Harvesting
Lure targeted user to enter credentials into a fake website
Note: No paswords are collected

Attachment
Lure targeted user to open an attachment within an email
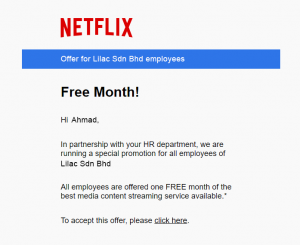

STEP 1
ASSESS


Phishing
Lure targeted user to click on a link in an email

Attachment
Lure targeted user to open an attachment within an email

Credential Harvesting
Lure targeted user to enter credentials into a fake website. Note: No paswords are collected


STEP 1
ASSESS

Phishing
Lure targeted user to click on a link in an email

Attachment
Lure targeted user to open an attachment within an email

Credential Harvesting
Lure targeted user to enter credentials into a fake website. Note: No paswords are collected



STEP 2
EDUCATE

Monthly Simulation
This is done on a consistent basis which makes safety the top priority in your employees' mind, ensuring they are always on the lookout for cyber threats while surfing the Internet or going through their emails.

Assessments
Short Quiz/Test after training helps ensure that your employees understand the basic mechanisms of the training modules and are always prepared.
STEP 2
EDUCATE

Monthly Simulation
This is done on a consistent basis which makes safety the top priority in your employees' mind, ensuring they are always on the lookout for cyber threats while surfing the Internet or going through their emails.

Assessments
Short Quiz/Test after training helps ensure that your employees understand the basic mechanisms of the training modules and are always prepared.
STEP 3
REINFORCE
STEP 3
REINFORCE
STEP 3
REINFORCE
STEP 4
MEASURE

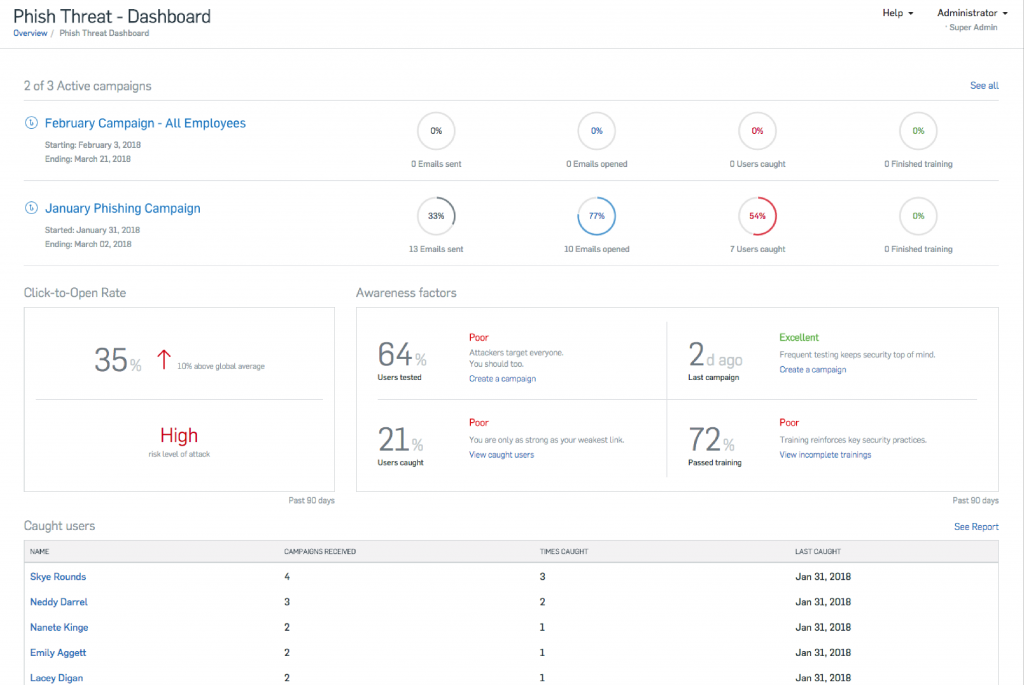
Phishing Simulation
Number of employees that opened dangerous attachment, clicked on a phishing link, read the training message completely and etc.

Online Learning Module
Number of employees who started the training, those that completed, those in progress.

Assessments
The scores by each staff, department or company as whole.
STEP 4
MEASURE

Phishing Simulation
Number of employees that opened dangerous attachment, clicked on a phishing link, read the training message completely and etc.

Online Learning Module
Number of employees who started the training, those that completed, those in progress.

Assessments
The scores by each staff, department or company as whole.
STEP 4
MEASURE

Phishing Simulation
Number of employees that opened dangerous attachment, clicked on a phishing link, read the training message completely and etc.

Online Learning Module
Number of employees who started the training, those that completed, those in progress.

Assessments
The scores by each staff, department or company as whole.


Social Engineering
Social engineering, in the context of information security, refers to psychological manipulation of people into performing actions or divulging confidential information.
Criminals use social engineering tactics because it is usually easier to exploit your natural inclination to trust than it is to discover ways to hack your software. For example, it is much easier to fool someone into giving you their password than it is for you to try hacking their password (unless the password is really weak).